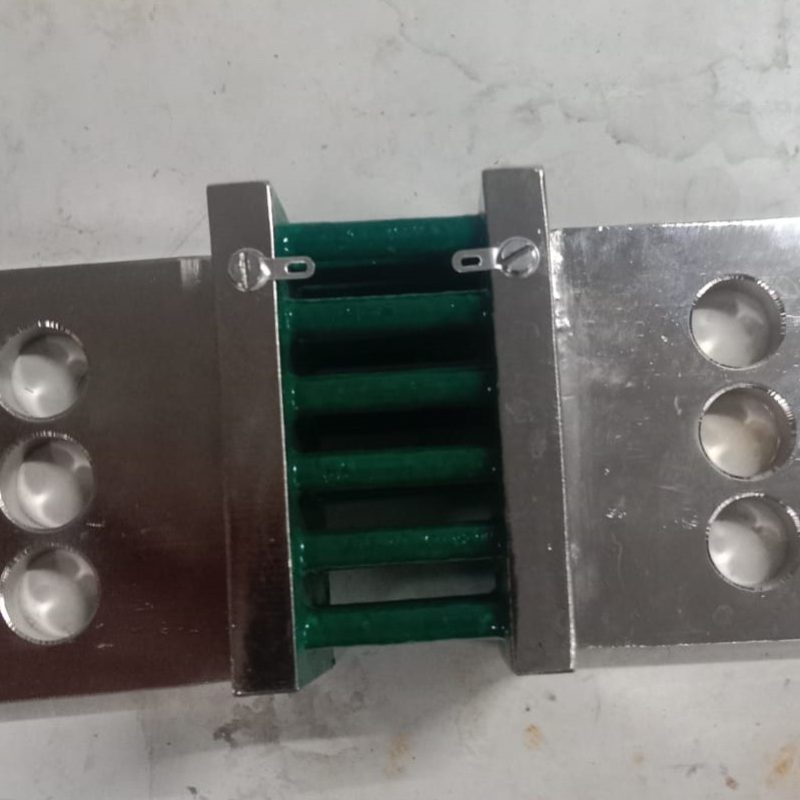
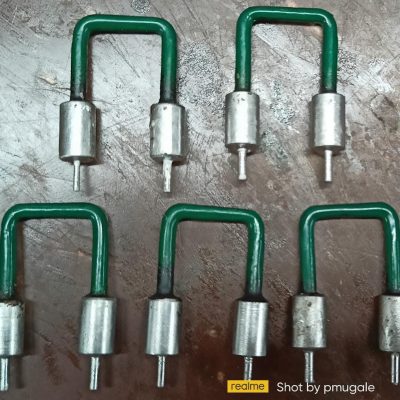
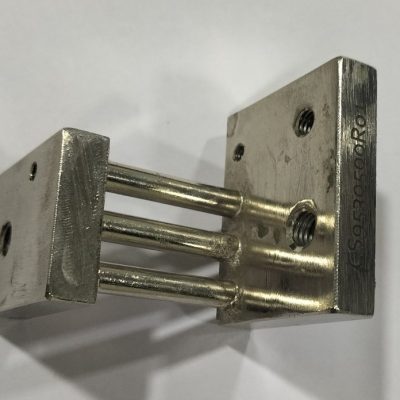
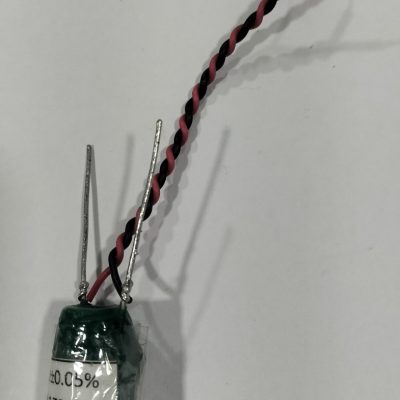
What are Shunts?
Shunts – as the name indicates – is a specific type of resistor designed tosend a millivolt output to a meter, or other instrument, that is in proportion tothe current flowing through the shunt. It consists of an electrical element thatcreates a low resistance path in a circuit and allows the current to flow throughit. A shunt is used for measuring the amount of current flowing through it. It isalso used in circuits to protect from overvoltage.
Shunts are used commonly in applications such as over-current protection, battery charging and H-bridge, and redirection of high-frequency noise, to name a few. Due to the application of Ohm’s law, aresistor is usually placed in parallel with the ammeter. As a result, there is a division of current, thuspermitting the measurement of ampere levels
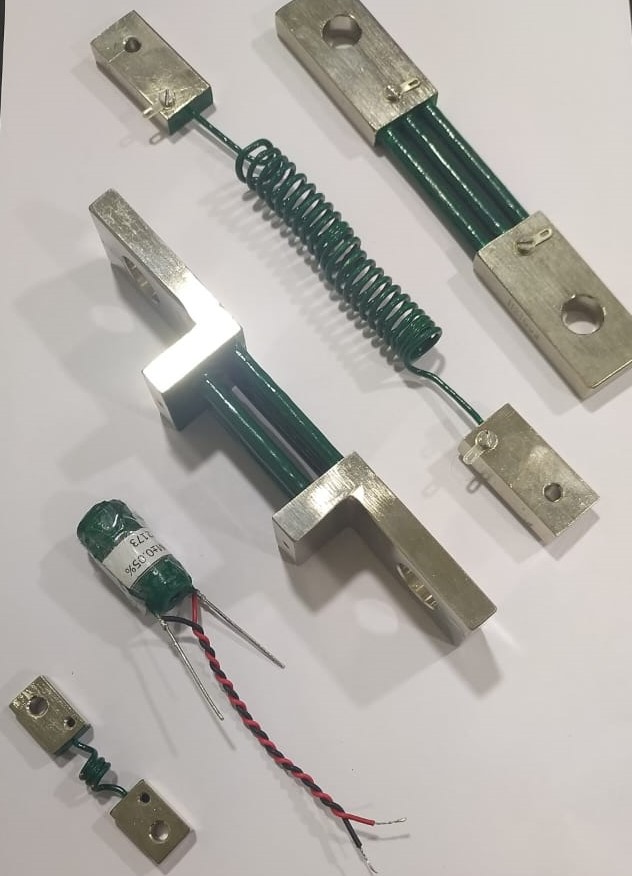
Precision DC Shunts
Specifications | Accuracy (%) | Rate (₹) |
|---|---|---|
300A 75MV | 0.5 | 656 |
25A 25MV/1ME | 0.05 | 315 |
1A/1V/1E | 0.05 | 315 |
2A 2V 1E | 0.05 | 315 |
1 MILLI OHM/1A | 0.5 | 315 |
2 MILLI OHM/1A | 0.5 | 84 |
5 MILLI OHM/1A | 0.5 | 105 |
10 MILLI OHM/1A | 0.5 | 126 |
20 MILLI OHM/1A | 0.5 | 158 |
50 MILLI OHM/1A | 0.5 | 189 |
Welding DC Shunts
Amperes | Voltage | Rate (₹) |
|---|---|---|
250 | 75 | 280 |
300 | 75 | 300 |
400 | 75 | 330 |
500 | 75 | 350 |
600 | 75 | 400 |
800 | 75 | 900 |
1000 | 75 | 1200 |
1500 | 75 | 2500 |
IS 1248 Standard DC Shunts
Amperes | Voltage | Rate (₹) |
|---|---|---|
5 | 160 | 600 |
10 | 160 | 750 |
15 | 170 | 800 |
20 | 180 | 1000 |
25 | 190 | 1200 |
30 | 225 | 1500 |
40 | 250 | 2000 |
50 | 250 | 2500 |
60 | 280 | 3000 |
75 | 280 | 4000 |
100 | 320 | 5000 |
125 | 340 | 6000 |
150 | 360 | 7500 |
200 | 625 | 8000 |
250 | 780 | 10000 |
300 | 840 | As per request |
400 | 950 | As per request |
500 | 1050 | As per request |







